Run External Macros Action: runExternalMacros
The runExternalMacros action executes a macro function from an external macro file in an Excel workbook. This function is handy for automating complex tasks and workflows that rely on pre-written macros.
Note: Ensure that the file being used is not open during the Case execution to avoid errors or conflicts.
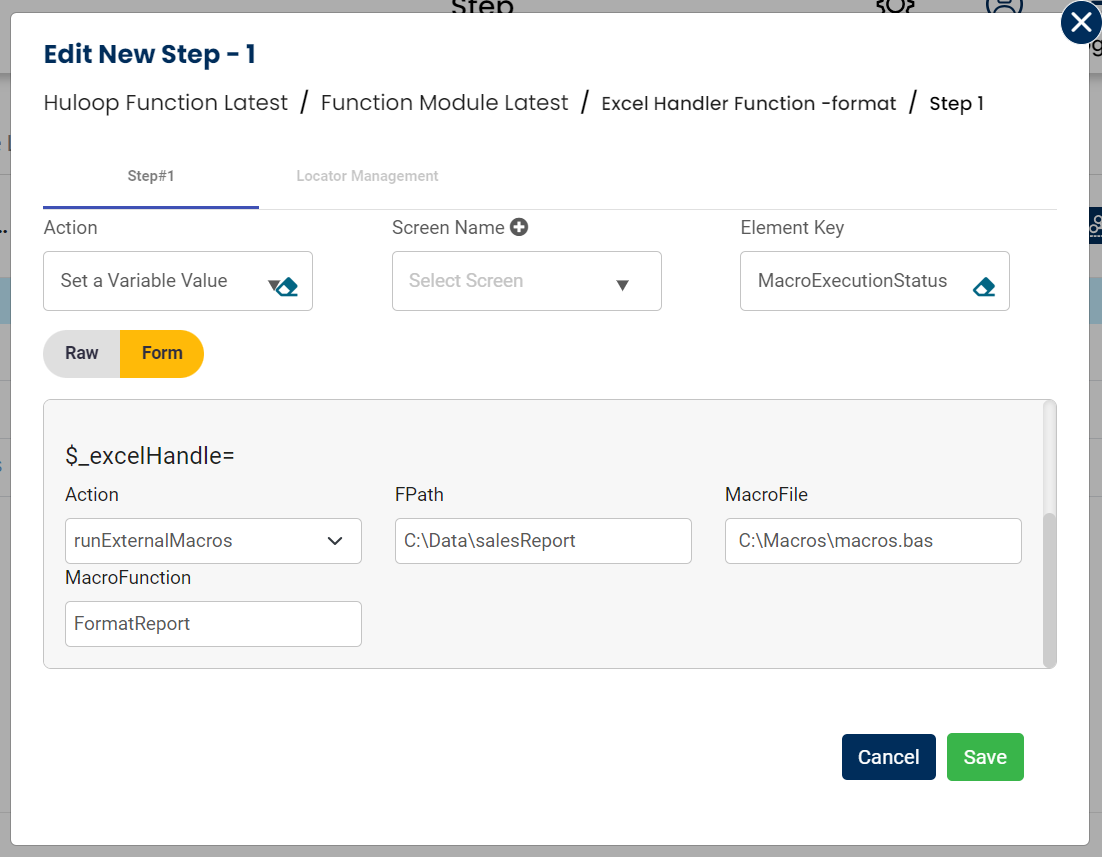
Example: You have an Excel file named salesReport.xlsx, a macro file macros.bas, and a macro function FormatReport that needs to be executed.
Steps to Configure:
- Add a new step.
- Select Set a Variable Value from the Action dropdown.
- Enter a variable name in the Element Key field (e.g., MacroExecutionStatus). This variable will store the operation result (e.g., success or failure).
- Click on Form, select Functions, and choose EXCEL Handler Functions from the dropdown.
- In the Cmd field, select runExternalMacros and provide the following parameters:
- FPath: Specify the path to the Excel file where the macro will run (e.g., C:\Data\salesReport.xlsx).
- MacroFile: Specify the path to the external macro file (e.g., C:\Macros\macros.bas).
- MacroFunction: Specify the macro function name to execute (e.g., FormatReport).
- Click Save.
Outcome on Execution:
- The action executes the specified macro function from the external macro file in the given Excel workbook.
- If the operation is successful, the action returns true in the variable defined in the Element Key (e.g., MacroExecutionStatus).
- If the operation fails (e.g., file not found, invalid macro function, or execution errors), it returns false.
- This variable can be referenced in later steps of your automation process using the syntax ${VariableName} (e.g., ${MacroExecutionStatus}).
